Successfully navigating the Voluntary Carbon Market (VCM) requires a deep understanding of the factors that drive carbon credit prices. At Abatable, we have developed a robust methodology to assess and inform our carbon credit valuation services, including a new tool designed to estimate carbon credit prices and break down the key factors influencing them.
Carbon credit prices are dynamic, fluctuating based on a range of variables, from project-specific attributes to broader market dynamics. In the VCM, price transparency is limited, with transaction details often kept private, abstract and anonymous.
As part of our work, we have collected around 51,500+ pricing data points across a diverse set of projects. These include exclusive pricing offers directly from developers who participate in our sourcing platform, trades and partner marketplace data.
To estimate the price of a specific project while maintaining anonymity, we group similar projects by type, continent, and registry, which users can search to receive pricing information.
The key drivers of carbon credit prices
Understanding these drivers is crucial for making informed decisions in the carbon market. Here are the six key factors that shape carbon credit pricing:
1. Quality risk
Quality risk significantly impacts the price of carbon credits. The credibility of a project, influenced by factors such as transparency, additionality, and long-term monitoring, affects buyer and investor confidence. Projects with lower quality risk tend to command higher prices. Conversely, concerns over permanence, leakage, or over-crediting can reduce valuations.
We use Abatable’s Project Quality Screening Tool to assess project quality, applying a numerical score based on factors like verified co-benefits (e.g., biodiversity or community development) and the risk of reversal. Higher-quality credits are more attractive to buyers and often command premium pricing.
2. Methodology used
The methodology behind carbon credit generation plays a crucial role in determining price. Some methodologies, such as afforestation or direct air capture, are more expensive due to technological complexity or long-term impact. Others, like certain renewable energy projects, may be priced lower due to wider availability and additionality concerns. Buyers often seek methodologies that align with their sustainability goals and risk appetite.
3. Country of origin
Geographic location affects pricing due to differences in regulatory environments, economic conditions, and political stability. Credits from jurisdictions with strong governance, clear regulations, and robust verification standards tend to attract higher prices. Conversely, credits from countries with political uncertainty or weak enforcement may trade at a discount.
4. Additional certifications
Beyond standard verification, additional certifications like Verra’s Climate, Community and Biodiversity (CCB) or Sustainable Development Verified Impact Standard (SD VISta) can enhance a carbon credit’s value. These certifications indicate co-benefits such as biodiversity conservation or community development, making them more attractive to buyers supporting broader sustainability objectives.
5. Volume
Like many commodities, carbon credits exhibit price sensitivity based on volume. Bulk purchases often secure discounts, while smaller purchases may come at a premium, especially for high-quality or niche projects with limited availability.
6. Credit vintage
The age of a carbon credit, or its vintage, affects its market price. Newer credits from recent projects often bring higher prices because they align with current scientific understanding and corporate reporting standards. Older vintages may trade at a discount, as they could be perceived as less relevant to present-day carbon reduction efforts.
Understanding carbon price variability
While these six factors provide a structured approach to price assessment, carbon credit prices are nevertheless also influenced by market conditions, demand trends, and regulatory changes. Buyers and investors should continuously monitor these variables to make informed purchasing decisions.
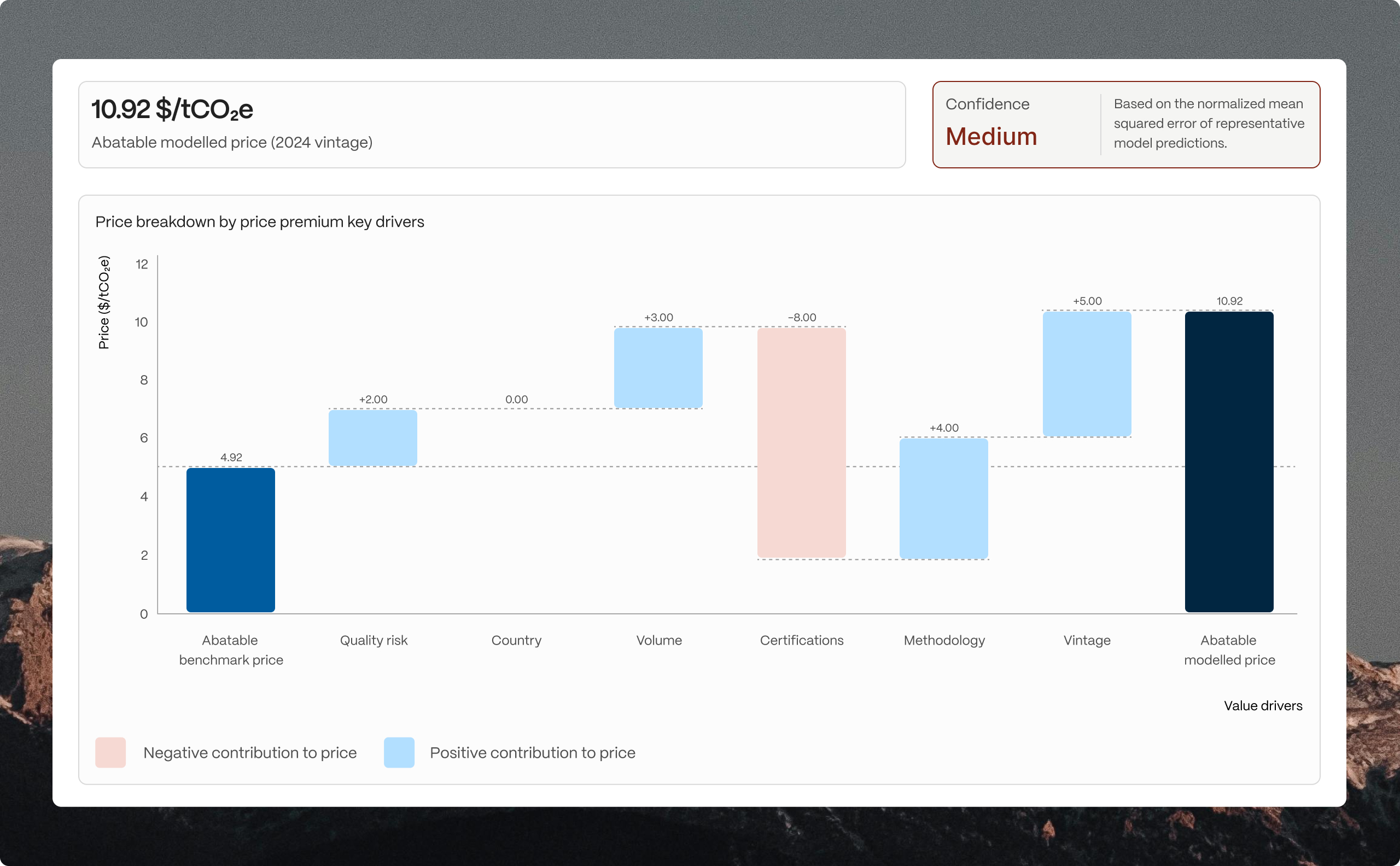
At Abatable, we simplify this complexity through our Portfolio Valuation module, which estimates the value of carbon credit portfolios using a sophisticated pricing methodology. This tool provides three key estimated price summaries:
- The Abatable benchmark price;
- The average price from the five most similar projects; and
- The Abatable modelled price, which uses machine learning to estimate prices based on project attributes.
Explore our Portfolio Valuation module
To gain deeper insights into your portfolio’s value and stay abreast of the latest carbon market developments, explore our Portfolio Valuation module today. Our new tool is designed to help you navigate the complexities of carbon credit pricing and make strategic, informed decisions in the VCM. By leveraging our expertise and technology, you can optimise your carbon credit investments and contribute to a more sustainable future.